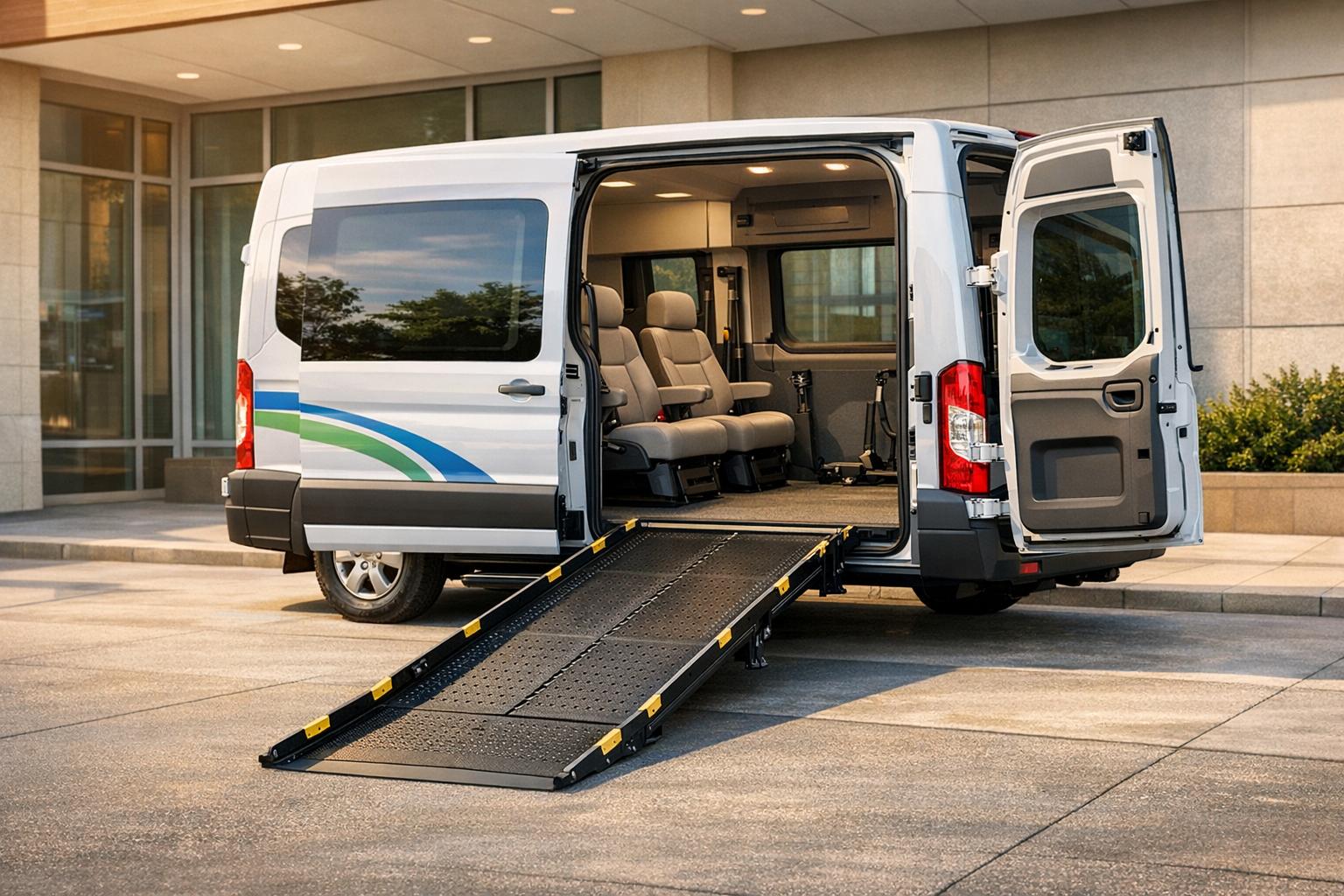
Designing a Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) fleet requires balancing accessibility, comfort, and compliance with federal and state regulations. Here’s what matters most:
- Accessibility Standards: Federal ADA guidelines (49 CFR Parts 37 and 38) require wheelchair lifts rated for 600 pounds, non-slip surfaces, and securement points. Many providers exceed these standards with 800-pound lifts and larger interior spaces.
- Fleet Composition: Wheelchair users account for 20–30% of trips, so fleets often include a mix of medical transport options including sedans, SUVs, and wheelchair-accessible vehicles to meet diverse needs.
- Passenger Comfort: Features like advanced HVAC systems, noise reduction, and flexible seating improve the rider experience.
- Compliance: In Texas, NEMT providers must meet state-specific HHSC rules, such as mandatory fire extinguishers, safety partitions, and driver background checks.
- Technology: AI-powered scheduling, real-time GPS tracking, and preventive maintenance tools optimize efficiency and safety.
- Driver Training: Drivers are trained in ADA compliance, safety protocols, and respectful communication to ensure quality service.
This article explores how these elements come together to create reliable, accessible, and comfortable NEMT services.
Top 7 Critical Mistakes New NEMT Providers Must Avoid to Achieve 6-Figure Success
ADA-Compliant Vehicles for Accessibility
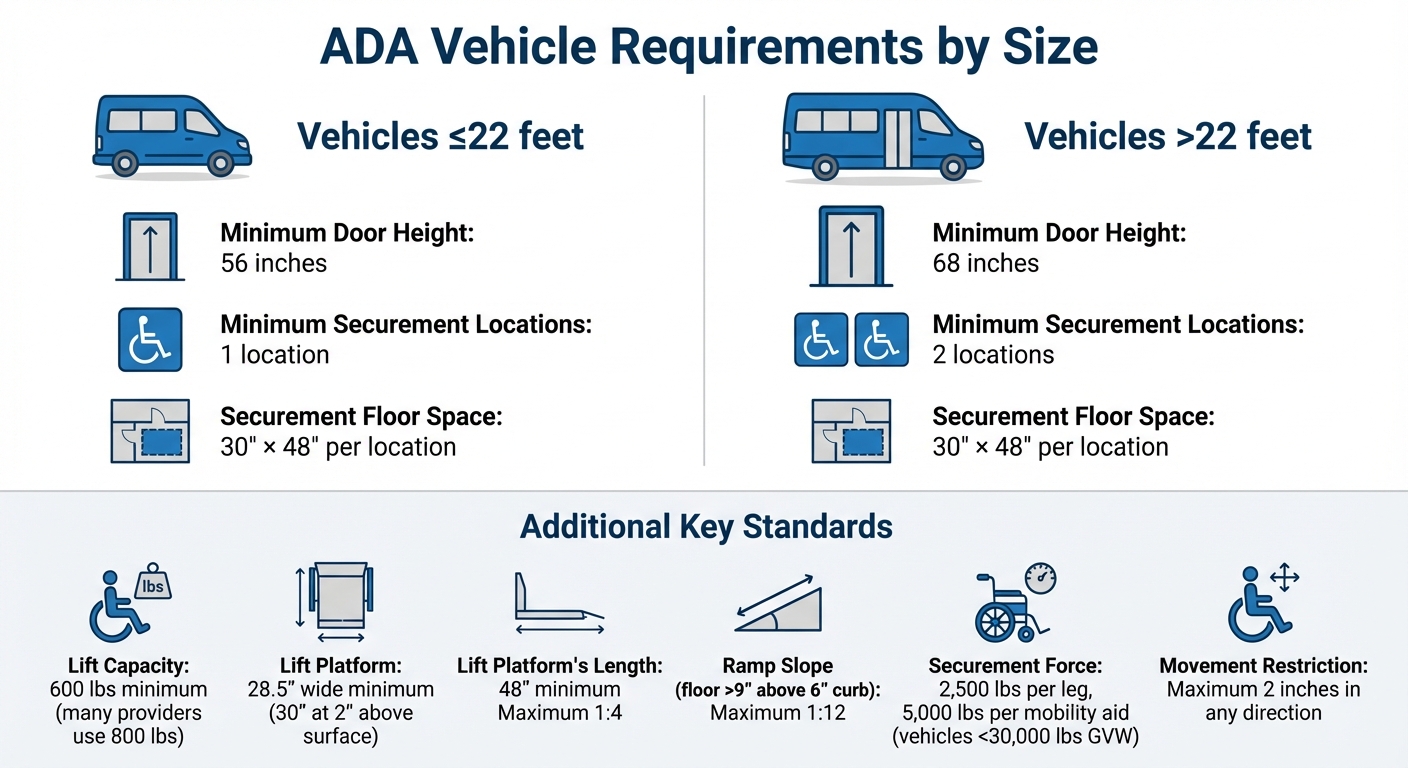
ADA Vehicle Requirements by Size: Door Heights and Securement Standards
Federal regulations outlined in 49 CFR Parts 37 and 38 establish the minimum standards for making non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) vehicles accessible. These vehicles must include a lift or ramp capable of handling at least 600 pounds. The lift platform must be at least 28.5 inches wide at the surface and expand to 30 inches wide when measured 2 inches above the platform, with a minimum clear length of 48 inches . Safety is prioritized with cables and pulleys requiring a safety factor of six based on their ultimate strength, while non-working components like platform frames must meet a safety factor of three. Lighting is also crucial, with stepwells and doorways needing at least 2 foot-candles of illumination when open, and the street surface requiring at least 1 foot-candle .
Door height requirements depend on the vehicle’s size. Larger vehicles, over 22 feet, must have a minimum overhead clearance of 68 inches, while smaller vehicles need at least 56 inches . Additionally, all aisles, steps, and securement floors must have non-slip surfaces, and step edges should feature a high-contrast color band for passengers with visual impairments . Once a mobility device is secured, it should remain stable, with movement restricted to no more than 2 inches in any direction . These baseline specifications pave the way for further ADA-specific requirements.
ADA Requirements for NEMT Vehicles
The number of securement locations in a vehicle is determined by its length. Vehicles over 22 feet must provide at least two securement locations, each with a clear floor space of 30 by 48 inches, while smaller vehicles (22 feet or less) require at least one . For vehicles with a gross vehicle weight rating under 30,000 pounds, securement systems must withstand a force of 2,500 pounds per securement leg and at least 5,000 pounds per mobility aid . Ramp slopes are also regulated: when deployed to ground level, ramps cannot exceed a 1:4 slope. If the vehicle floor is more than 9 inches above a 6-inch curb, the slope must not be steeper than 1:12 . Many providers now use "kneeling" systems, which lower the vehicle’s front end to ensure compliant ramp slopes and improve the boarding process.
"Transit agencies that acquire vehicles that can accommodate larger dimensions and heavier weight loads will be able to accommodate more individuals and their larger mobility devices." – National RTAP
Although the federal standard for lift capacity is 600 pounds, many providers opt for 800-pound lifts to better serve passengers using heavier power wheelchairs or those with bariatric needs . Beyond meeting technical standards, thoughtful design choices can greatly influence rider comfort and overall accessibility.
Wheelchair and Stretcher Accessibility
Side-entry designs are often preferred over rear-entry configurations because they provide a smoother ride, avoiding the discomfort of sitting behind the rear axle. To ensure wheelchair transport safety, lifts must interlock with the vehicle’s brakes, transmission, or doors to prevent movement during deployment. The speed of an occupied lift platform is capped at 6 inches per second, with horizontal and vertical acceleration limited to 0.3g .
Handrails, positioned between 30 and 38 inches, assist passengers using canes or walkers. These handrails must withstand a force of at least 100 pounds . Passengers should also have the option to board the lift facing either toward or away from the vehicle.
For stretcher transport, providers may need to modify floor plans to accommodate gurneys and oxygen tanks, which could influence the choice between full-size vans and minivans. Flip seats in the securement area offer flexibility, allowing the space to be used for ambulatory passengers when no wheelchair is present. This approach maximizes fleet efficiency while adhering to ADA standards .
| Vehicle Size | Minimum Door Height | Minimum Securement Locations |
|---|---|---|
| ≤22 feet | 56 inches | 1 location |
| >22 feet | 68 inches | 2 locations |
Routine maintenance is critical. Operators should test the lift or ramp during every pre-trip inspection to ensure it works properly. If a passenger’s combined weight with their wheelchair exceeds the lift’s capacity, agencies should evaluate the situation individually and, if possible, offer the option for the passenger to board separately with assistance from a personal care assistant.
Passenger Comfort in NEMT Vehicles
While meeting ADA compliance is essential, creating a genuinely comfortable ride goes beyond just meeting legal standards. With about 63.5% of NEMT trip requests coming from ambulatory passengers and 30.3% from wheelchair users, vehicles need to strike a balance between adaptability and specialized features. Prioritizing comfort not only meets these diverse needs but also elevates the overall passenger experience.
Interior Design Features
Interior flexibility is key. Features like foldable or removable seating configurations allow vehicles to accommodate both ambulatory and wheelchair passengers seamlessly. For longer trips, captain’s chairs offer a higher level of comfort, while bench seating can maximize capacity when transporting larger groups.
Temperature control is another critical aspect. Standard factory HVAC systems often fall short in maintaining consistent cabin temperatures, especially in modified vehicles with extended roofs or lowered floors. Enhanced climate control systems with additional vents help regulate the cabin environment, ensuring sensitive passengers remain comfortable throughout the journey.
Additional amenities can make a big difference. Secure storage compartments keep personal items safe and accessible, while charging ports allow passengers to power their devices or medical equipment during long trips. Intercom systems and emergency buttons improve communication between passengers and drivers, which can be crucial during extended rides or emergencies. Seat belt extensions are another thoughtful touch, ensuring safety for passengers who require larger accommodations.
Noise Reduction and Suspension Systems
Beyond the interior, the vehicle’s overall dynamics significantly affect passenger comfort. Most NEMT vehicles start as standard passenger or cargo vans, which aren’t originally designed for medical transport. Converting these vehicles involves making intentional upgrades to reduce road vibrations and cabin noise – both of which can impact physical and psychological comfort.
Modern securement systems, such as those from Q’STRAINT and Sure-Lok, not only enhance safety but also improve comfort by absorbing road shocks and vibrations. This feature is particularly important for stretcher patients who need to remain lying down throughout the trip. In areas with rougher roads, some operators prefer SUVs over standard vans for their advanced suspension systems, which provide a smoother ride.
"Comfort extends beyond physical well-being, embracing the environment within the vehicle. Adjusting temperature and noise levels as per passenger preferences ensures a ride tailored to their comfort." – Tobi
Routine inspections of suspension systems and hydraulic lifts are essential to minimize noise and vibration. Drivers should also be trained to adjust cabin settings based on passenger sensitivities and preferences. These thoughtful adjustments transform NEMT services from basic transportation into a more personalized and comfortable care experience. By focusing on these details, operators can ensure a level of service that supports both accessibility and passenger well-being.
Texas NEMT Fleet Regulations
Running a Texas Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) fleet means adhering to specific rules set by the Texas Health and Human Services Commission (HHSC). These regulations go beyond federal ADA standards, shaping how providers manage vehicles, train drivers, and document services. Knowing these requirements is key – not just to avoid penalties, but also to ensure your fleet operates legally and serves Medicaid clients effectively. Together, these state and federal guidelines aim to uphold safety and quality care.
Texas Health and Human Services Commission (HHSC) Standards
The HHSC outlines clear expectations for driver qualifications, vehicle requirements, and Medicaid-related processes. Here are the essentials:
- Driver Requirements: Drivers must be at least 19 years old, hold a valid Texas driver’s license, and pass background checks that exclude serious criminal offenses.
- Vehicle Standards: Vehicles need current Texas registration, working climate control, and specific safety features like:
- A one-quart fire extinguisher stored in the driver’s area.
- Locks to prevent passengers from exiting while the vehicle is moving.
- A safety partition separating the driver from passengers.
- A fully functional two-way communication system.
- Medicaid Procedures: Providers must enroll with Texas Medicaid & Healthcare Partnership (TMHP) and secure HHSC pre-authorizations to qualify for reimbursement. Claims deadlines differ: in-state providers have 95 days from the service date, while out-of-state providers get up to 365 days. Additionally, trips over 150 miles one-way or 300 miles round-trip are classified as long-distance travel.
These regulations form the foundation for the safe medical transport practices that all Texas NEMT providers must follow.
Safety and Maintenance Guidelines
Texas law requires regular maintenance to keep vehicles in top working condition. Functional climate control systems are non-negotiable to ensure passenger safety and comfort during transport. For wheelchair-accessible vehicles, there are even more specific requirements:
- Lifts or ramps must be powered (electric or hydraulic) with non-skid surfaces.
- Securement systems must prevent all movement – sideways, forward, backward, or vertical.
- Rear-view mirrors should allow drivers to monitor passengers at all times.
- An emergency exit at the back of the vehicle is mandatory.
Failing to meet these standards can result in serious consequences, including financial penalties, contract termination, and exclusion from Medicaid and Medicare programs. As Mitch Cooper, a writer for Tobi, explains:
"The repercussions of non-compliance can be severe, impacting both your financial stability and legal standing." – Mitch Cooper
Additionally, services provided by unqualified drivers or in non-compliant vehicles won’t be eligible for Medicaid reimbursement. Providers excluded from one state’s Medicaid program are automatically barred from all states’ Medicaid and Medicare programs.
Pre-trip inspections are critical. Drivers must confirm the presence of a one-quart fire extinguisher and test the communication system before starting any trip. Providers should also keep thorough records to satisfy HHSC and TMHP reviews. This includes maintaining prior authorization documents and ensuring records for clients under 21 are preserved until the HHSC provides notification.
sbb-itb-8e5d2ef
Technology for Safety and Efficiency
Modern Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) operations depend on technology to solve challenges that manual systems can’t handle effectively. Managing numerous trips across Austin, coordinating wheelchair-accessible vehicles with ambulatory rides, and adapting to last-minute changes can overwhelm traditional methods. With the right software, fleets can operate more efficiently – lowering costs, enhancing safety, and creating a smoother experience for passengers. These innovations align with the commitment to comfort and accessibility by streamlining processes and boosting safety measures.
AI-Powered Scheduling and Route Optimization
AI-driven scheduling processes massive amounts of data in seconds – factoring in pickup locations, appointment times, vehicle types, wheelchair accessibility, and real-time traffic conditions. This smart matching ensures that the appropriate vehicle reaches the right passenger on time. Zyvra Mobility utilizes AI-based scheduling and routing tools to handle complex trip combinations automatically, minimizing manual errors and delays.
The benefits are clear: automated route planning can cut operational costs by 20% to 30%, while AI-powered scheduling reduces travel times and no-shows by up to 40%. On-time arrivals improve by up to 50% compared to traditional dispatching methods. Driver utilization rates jump from under 60% with manual routing to over 85% when automation is in place. Additionally, advanced routing systems help fleets save 15% to 25% on fuel expenses and reduce "deadhead miles" – empty trips without passengers – by 30%.
Multi-loading capabilities further enhance efficiency by grouping compatible trips into a single route whenever possible. By considering the diverse mix of ambulatory and wheelchair-accessible requests, smart software maximizes vehicle capacity without compromising service standards. Dynamic scheduling also adapts to last-minute cancellations or new requests, updating driver schedules automatically to minimize downtime and keep operations running smoothly. Beyond scheduling, real-time tracking ensures safety and precision for every trip.
Real-Time Tracking and Fleet Management
Real-time tracking builds on intelligent scheduling to improve fleet efficiency and passenger safety. GPS tracking provides dispatchers with instant visibility into vehicle locations, enabling them to monitor route compliance and give passengers accurate ETAs. This feature goes beyond simply locating vehicles – it ensures safety and operational transparency throughout the journey.
Fleet management systems also track driver behavior, such as speeding, harsh braking, or rapid acceleration. Providers can use this data to implement targeted safety training and reduce accident risks. As NEMT Cloud Dispatch highlights:
"Real-time GPS tracking is a critical feature for any fleet management solution. It allows you to monitor the location of your vehicles in real-time, providing insights into driver behavior, route efficiency, and vehicle utilization."
Preventive maintenance alerts use vehicle mileage and engine health data to send reminders for essential upkeep, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and inspections, helping avoid mechanical failures. These alerts also cover driver credentialing expirations and vehicle registration renewals, which are essential for maintaining compliance with Texas HHSC regulations. Digital logs further enhance accuracy for Medicaid billing by documenting routes, trip times, and mileage for reimbursement claims.
Automated passenger notifications play a key role in reducing anxiety and improving trust. These updates keep passengers, drivers, and dispatchers informed, significantly lowering no-show rates. MediRoutes explains:
"With real-time alerts, patients receive reminders or updates if there’s a change in their ride schedule. This reduces no-shows and helps build trust between the patient and provider."
When passengers know exactly when their ride will arrive, they’re more likely to be ready, boosting efficiency across the entire operation.
Driver Training for Comfort and Accessibility
While technology can streamline routes and improve tracking, drivers are the heart and soul of Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT). They ensure passengers receive safe, respectful assistance and operate equipment correctly. Every year, about 3.6 million people miss or delay medical appointments because of transportation issues, and over 37,000 older adults are injured while entering or exiting vehicles. Professional driver training programs address these challenges by equipping drivers with the skills needed to meet diverse passenger needs while upholding top safety standards.
Incorporating advanced technology is important, but ensuring drivers are well-trained remains key to providing comfortable and accessible service.
Driver Certification and Background Checks
To qualify as an NEMT driver, individuals must be at least 18 years old, hold a valid driver’s license, and maintain a clean driving record. Beyond these basic requirements, drivers are required to pass a physical medical exam to confirm they can handle the job’s demands, such as assisting passengers and operating heavy equipment like wheelchair lifts.
Background checks are another critical step. Initial and ongoing screenings through agencies like the DOJ or FBI help identify any felonies, sex offenses, or other disqualifying conduct. The California DMV highlights the importance of these checks:
"The reason for a certificate denial or revocation does not need to be directly related to driving. Instead, the reason may be related to the vulnerable nature of the passengers."
In some regions, drivers also need specialized certifications. For example, California offers credentials like the General Public Paratransit Vehicle (GPPV) certificate, Vehicle for Developmentally Disabled Persons (VDDP) certificate, or Ambulance Driver Certificate. Interestingly, even a single 2-point conviction, such as reckless driving, can result in the revocation of a specialized driving certificate in California, even if the standard Class C license remains valid.
Training Programs for Passenger Needs
Once certified, drivers undergo extensive training designed specifically for NEMT services. Safety modules cover defensive driving, emergency response protocols, and essential First Aid and CPR skills. As Nygel Varghese, a Content Producer, explains:
"Learning first aid and CPR equips drivers with life-saving skills for those unforeseen medical emergencies during a ride. These lessons transform them from drivers into caretakers."
Accessibility training is equally important. Drivers are taught how to safely assist passengers with ramps and operate securement systems in compliance with ADA requirements. Pre-trip inspections include testing equipment like wheelchair lifts to ensure everything is fully operational before service begins.
Respect and effective communication are integral to these training programs. Drivers learn to treat passengers with courtesy, use person-first language (e.g., "person with a disability"), and communicate directly with the passenger rather than their companion. They’re trained to ask before assisting and to avoid touching mobility devices like wheelchairs or canes without permission. For passengers with hearing impairments, drivers are instructed to face them directly for lip-reading and to avoid shouting. For those with visual impairments, drivers introduce themselves verbally and announce all stops.
The U.S. Department of Transportation emphasizes the importance of these practices:
"Each public or private entity which operates a fixed route or demand responsive system shall ensure that personnel are trained to proficiency… so that they operate vehicles and equipment safely and properly assist and treat individuals with disabilities who use the service in a respectful and courteous way."
To maintain these high standards, regular monitoring and evaluations are conducted. This includes reviewing driver logs, conducting surprise drug and alcohol tests, and requiring periodic license renewals with refresher courses. When combined with advanced fleet features, this rigorous training ensures every passenger enjoys a safe, comfortable, and accessible journey.
Conclusion
Creating an effective NEMT fleet means finding the right balance between accessibility, comfort, and technology. Start with ADA-compliant vehicles equipped with lifts that exceed the 600-pound minimum to accommodate bariatric passengers and heavy power chairs. A well-rounded fleet – featuring minivans for routine trips, midsize wheelchair-accessible vans for small groups, and specialized stretcher vehicles for medical transfers – ensures flexibility to meet the needs of approximately 63.5% ambulatory riders and 30.3% wheelchair users.
But it’s not just about meeting technical requirements; rider comfort plays a critical role. This includes features like high-output HVAC systems and clean, well-maintained interiors, which create a professional and respectful environment for passengers. Folding seats in securement areas also allow vehicles to adapt quickly to different passenger configurations, enhancing fleet efficiency.
Technology is another key piece of the puzzle. AI-powered routing and real-time GPS tracking help reduce wait times, optimize fuel usage, and provide accurate ETAs. Regular preventive maintenance, based on mileage and engine hours, ensures vehicles remain safe and operational. Additionally, in-app messaging keeps passengers informed throughout their journey, improving the overall experience.
At Zyvra Mobility, providing NEMT in Round Rock and Austin, TX, these approaches come together to provide dependable transportation for medical appointments, hospital discharges, rehabilitation sessions, and specialist visits. With ADA-compliant vehicles, certified drivers, and advanced scheduling tools, Zyvra Mobility delivers reliable service for every passenger. By combining thoughtful fleet design, comprehensive driver training, and cutting-edge technology, they ensure accessibility and comfort are always front and center.
FAQs
What features make NEMT vehicles more comfortable for passengers?
Passenger comfort in non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) vehicles depends heavily on smart design and accessibility-focused features. Ergonomic seating with proper cushioning and adjustable options provides a stable and supportive ride, especially for passengers who may be more fragile or need additional care. Features like wide door openings and lowered floors make getting in and out of the vehicle much simpler, minimizing physical effort during transfers.
To further support accessibility, many NEMT vehicles are equipped with wheelchair ramps or lifts and securement systems that keep mobility devices safely in place while maintaining a roomy cabin. Additionally, modern vehicles often include technology upgrades such as GPS-enabled dispatch systems, onboard communication tools, and safety monitoring equipment. These advancements streamline trips, cut down on wait times, and create a smoother, more reliable experience for passengers, offering both comfort and reassurance.
How do ADA regulations impact the design of NEMT vehicles?
ADA regulations are essential in designing non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) vehicles, ensuring they meet the needs of all passengers. These rules mandate features like wheelchair-accessible ramps or lifts, spacious interiors, secure systems for mobility devices, and low-floor entry designs to accommodate individuals with various mobility requirements.
Federal standards, such as 49 CFR Part 38, specify detailed design elements, including minimum door widths, ramp weight capacities, and safety features. Operational tools like the ADA Toolkit further emphasize practical considerations, such as secure tie-downs for wheelchairs, adequate turning space, and layouts that can accommodate stretchers. Together, these guidelines ensure that NEMT vehicles are equipped to offer safe and comfortable transportation.
By following ADA standards, NEMT providers not only stay compliant with the law but also prioritize accessibility, making it a core part of their service commitment.
What technologies help improve efficiency and safety in NEMT operations?
Modern non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) services are leveraging cutting-edge technology to improve both safety and efficiency. Real-time GPS tracking and fleet management systems play a crucial role by letting dispatchers keep an eye on vehicle locations, adjust routes on the fly, and cut down on delays. On top of that, AI-driven maintenance tools help predict potential mechanical problems early, reducing the chances of breakdowns and keeping vehicles dependable.
Specialized routing software takes the guesswork out of planning trips, creating safe and efficient routes that save time without compromising passenger safety. Meanwhile, Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) technology provides constant updates on vehicle positions, which helps streamline scheduling, improve dispatch decisions, and enhance reporting accuracy. Together, these technologies ensure a smooth and secure experience for both passengers and operators.




